Wi-Fi STA low power consumption guide
Power saving process
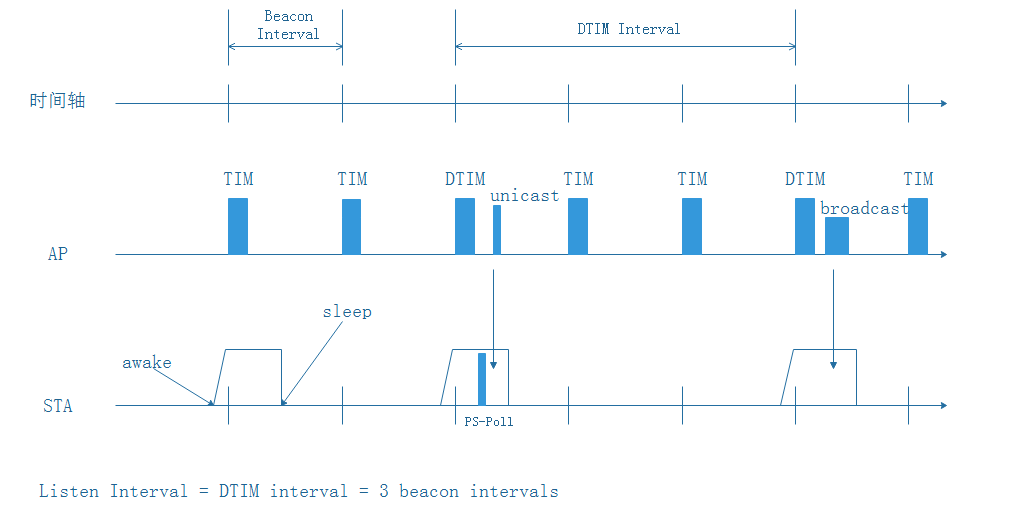
Based on DTIM
The typical power saving process is shown in the figure above.
- When STA connects to the AP, it exchanges key parameters related to sleep with the AP:
Beacon interval - AP periodically broadcasts beacon, and the beacon will indicate whether the dormant STA has unicast packets to receive.
DTIM interval - is an integer multiple of the beacon interval. The DTIM beacon will indicate whether there are broadcast packets to be sent, and broadcast packets will be sent in the subsequent beacon interval.
Listen Interval - When the STA is in sleep state, the maximum time required for the AP to cache unicast packets for the STA
When the sleep conditions are met (usually when the STA has no packets to send or receive), the STA notifies the AP that it will enter sleep mode.
After receiving confirmation from the AP, STA turns off the RF/MAC power or clock and enters sleep state.
When the STA is in sleep state, the AP will cache the unicast packets sent to the STA; if the AP has broadcast packets to send, it will notify the STA in the subsequent DTIM beacon.
The STA wakes up during the DTIM period and checks whether it needs to receive broadcast packets; if there is a broadcast, it wakes up to receive broadcast packets. If there are unicast packets to receive, it notifies the AP that it is awake, and then the AP sends a unicast packet to the STA.
STA sleeps and wakes up regularly. In sleep state, RF, MAC, and MODEM are theoretically turned off. In Wi-Fi and Bluetooth LE coexistence mode, RF may not be turned off.
Further reduce power consumption
From the Power Saving Process we can see that in sleep mode, STA must wake up every DTIM interval, which may become the main cause of power consumption in some scenarios, especially when the DTIM value is very small (such as When DTIM is 1) In order to reduce the frequency of STA waking up, BK provides a mechanism: waking up only at the listen interval. The process is as follows:

Based on Listen Interval
Applications can set the listen interval via power_save_set_listen_int(10).
Generally, the larger the listen interval, the better the energy saving effect, but the larger the listen interval, the worse the performance and connection stability.
Note
Because the AP will send broadcast frames in the DTIM interval, when the “wake up only in listen interval” mechanism is enabled, the STA may miss broadcast packets.
If the listen interval is set too long, it may cause the AP to cache too many unicast packets for STA. When the AP has insufficient memory, it may cause packet loss. Both situations will affect Wi-Fi performance and connection stability.
This mechanism is suitable for applications that do not have high performance requirements but particularly high power consumption requirements.
Disable power saving mode
STA sleep is enabled by default. The user can disable sleep through bk_wlan_mcu_ps_mode_disable() and bk_wlan_dtim_rf_ps_mode_disable(), and enable sleep through bk_wlan_dtim_rf_ps_mode_enable() and bk_wlan_mcu_ps_mode_enable(). Please note that for some specific applications, STA sleep has specific requirements, such as:
Important
When STA and AP coexist, due to the existence of AP, even if it is enabled, it will not actually enter low power consumption.
When STA and Bluetooth LE coexist, the sleep mode must be enabled. Because the STA RF should enter the sleep state first when switching to Bluetooth LE, otherwise packet loss may occur.
For devices that are not sensitive to power consumption, such as refrigerators, rice cookers, etc., you can choose to disable sleep for optimal performance.
Wi-Fi keep alive test
For Wi-Fi keep alive test, refer to:doc:/developer-guide/power_save/wifi_alive_test