Quick Start Guide
Take the development board BK7237 as an example, and demonstrate the use method through the project
Build Armino’s compilation environment
Method of configuring Project Armino
How to compile and download firmware
Preparation
Hardware:
Board BK7237
Serial port buring tool
PC(Windows & Ubuntu)
!Note:
Armino only supports compiling on Linux platform and firmware burning on Windows platform. Therefore, we need two computers, one Linux platform and one Windows platform. Of course, we can also install Linux virtual machine on Windows platform only
Software:
RISCV tool chain, used to compile the Armino RISCV version
Build tools, including CMake
Armino source code
Serial port burning software
Introdection to Development Board
Click the following link to learn more about the development boards supported by Armino:
Armino SDK Code download
We can download Armino from gitlab:
mkdir -p ~/armino
cd ~/armino
git clone http://gitlab.bekencorp.com/wifi/armino.git
We can also download Armino from github:
mkdir -p ~/armino
cd ~/armino
git clone https://github.com/bekencorp/armino.git
!Note:
- The latest SDK code is downloaded from gitlab on the official website, and
relevant accounts can be found on the project to review the application.
Build Compilation Environment
!Note:
- Armino, currently supports compiling in Linux environment. This chapter willtake Ubuntu 20.04 LTS
as an example to introduce the construction of the entire compiling environment.
Tool Chain Installation
BK7237 Tool download path:
Toolchain Download: http://dl.bekencorp.com/tools/toolchain/ Get the latest version in this directory, ps:toolchain_v5.1.1.tgz
After downloading the tool kit, decompress it to ‘/opt/risc-v’ through the following command:
$ sudo tar -zxvf toolchain_v5.1.1.tgz -C /
!Note:
- Tool chain the default path in the middleware/soc/bk7237/bk7237.defconfig file definition, customers can configure
CONFIG_TOOLCHAIN_PATH=”/opt/risc-v/nds32le-elf-mculib-v5/bin”
Program compilation depends on library installation
Enter the following command in the terminal to install pythonCMakeNinjacrypto:
sudo dpkg --add-architecture i386
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install build-essential cmake python3 python3-pip doxygen ninja-build libc6:i386 libstdc++6:i386 libncurses5-dev lib32z1 -y
sudo pip3 install pycrypto
Document Compilation Dependent Library Installation
Enter the following command on the terminal to install the python required for compiling the document:
sudo pip3 install sphinx_rtd_theme future breathe blockdiag sphinxcontrib-seqdiag sphinxcontrib-actdiag sphinxcontrib-nwdiag sphinxcontrib.blockdiag
Set Python default version:
sudo ln -s /usr/bin/python3 /usr/bin/python
Compilation project
Enter the following command in the terminal to compile the Armino default project. PROJECT is an optional parameter, which is app by default. The default project is to start WiFi, BLE, initialize common drivers, and start the Armino default Cli program:
cd ~/armino
make BK7237
BK7237 is a dual CPU core system, which is configured as dual core by default. When compiling the CPU0 system of BK7237 platform, CPU1 and CPU0 will be compiled automatically, and CPU0 and CPU1 systems will be packaged together
The default project of BK7237 platform uses FreeRTOS V10.4 system:
components/os_source/freertos_v10
BK7237 platform supports Hongmeng OS V3.0.1 system and can compile Harmony project:
cd ~/armino make BK7237 PROJECT=harmony
Of course, you can also compile any other project under armono/projects. The command is as follows:
cd ~/armino make BK7237 PROJECT=examples/get-started/hello_world
Configuration project
We can change the Armino default configuration item through menuconfig:
cd ~/armino make menuconfig
We can also directly use the project configuration file for differentiated configuration:
Project Profile Override Chip Profile Override Default Configuration Example: BK7237.config >> BK7237.defconfig >> KConfig + Example of project configuration file: projects/app/config/BK7237.config projects/harmony/config/BK7237.config projects/customization/BK7237_config1/config/BK7237.config + Sample chip configuration file: middleware/arch/BK7237/BK7237.defconfig + Sample KConfig configuration file: middleware/arch/riscv/Kconfig components/bk_cli/Kconfig- Important configuration instructions
The operating system is configured as FreeRTOS V10:
# # FreeRTOS # CONFIG_FREERTOS=y # CONFIG_LITEOS_M is not set CONFIG_FREERTOS_V9=n CONFIG_FREERTOS_V10=y
The operating system is configured as Hongmeng OS:
# LITEOS_M CONFIG_LITEOS_M_V3=y CONFIG_LITEOS_M_BK=y # FreeRTOS CONFIG_FREERTOS=n CONFIG_FREERTOS_V9=n CONFIG_FREERTOS_V10=n
Use and Difference of Series Chip Macros
Macro CONFIG_SOC_BK7256XX represents BK7237 series:
It belongs to BK7235/BK7237/BK7256 common chip macro. CPU1 also needs to define this macro collocation method:CONFIG_SOC_BK7256XX=yDistinguish macros of the same series of chips (not used to distinguish other chips):
CONFIG_SOC_BK7237, CPU1 needs to define the macro and CONFIG_ SLAVE_ CORE Combination Differentiation BK7237_ CPU1 collocation method:CONFIG_SOC_BK7237=y
Macro of string series chips (used to distinguish other chips during compilation):
cpu0/cpu1 distinguish: CPU0:CONFIG_SOC_STR="BK7237" CPU1:CONFIG_SOC_STR="BK7237_cp1"Dual core CPU0, CPU1 related macro differentiation (for code differentiation):
CONFIG_DUAL_CORE #Dual core function CONFIG_MASTER_CORE #Depends on CONFIG_ DUAL_ CORE, the difference between CPU0 and CPU1 CONFIG_SLAVE_CORE #Depends on CONFIG_ DUAL_ CORE, the difference between CPU0 and CPU1 Single core: none of the above three macros is defined
New project
The default project is projects/app. For new projects, please refer to projects/harmony project
Burn Code
On the Windows platform, Armino currently supports UART burning.
Burn through serial port
!note:
Armino supports UART burning. It is recommended to use the CH340 serial port tool board to download.
Serial port burning tool is shown in the figure below:

UART
Acquisition of burning tools:
http://dl.bekencorp.com/tools/flash/ Get the latest version in this directory. Ps:BEKEN_WRITER_V1.6.38_20220905.zip
bk_writer.exe The interface and related configurations are shown in the figure below:
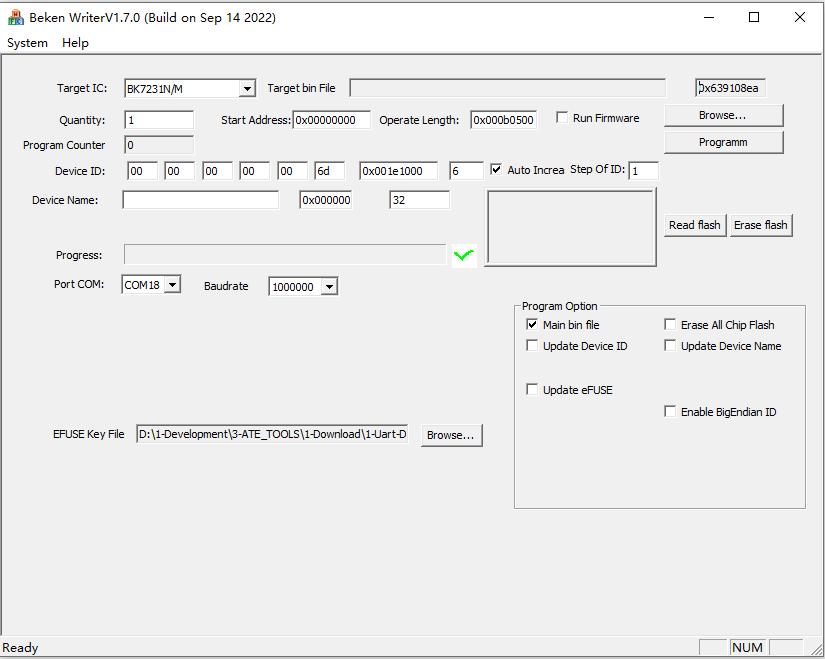
bkwriter GUI
Burn the serial port UART1, click “” Burn “” to burn the version, and then power down and restart the device after burning.
Serial port Log and Command Line
At present, on the BK7237 platform, the serial port Log and Command Line commands are input on the UART1 port; You can view the list of supported commands through the help command;
The log of CPU 1 is also output through the UART1 serial port of CPU 0, and the log of CPU 1 is marked with “cpu 1”;
Command Line of CPU1 can be executed through UART1 of CPU0, such as:
Cpu1 help//Output the command list of cpu1
Cpu1 time//Output the current running time of cpu1